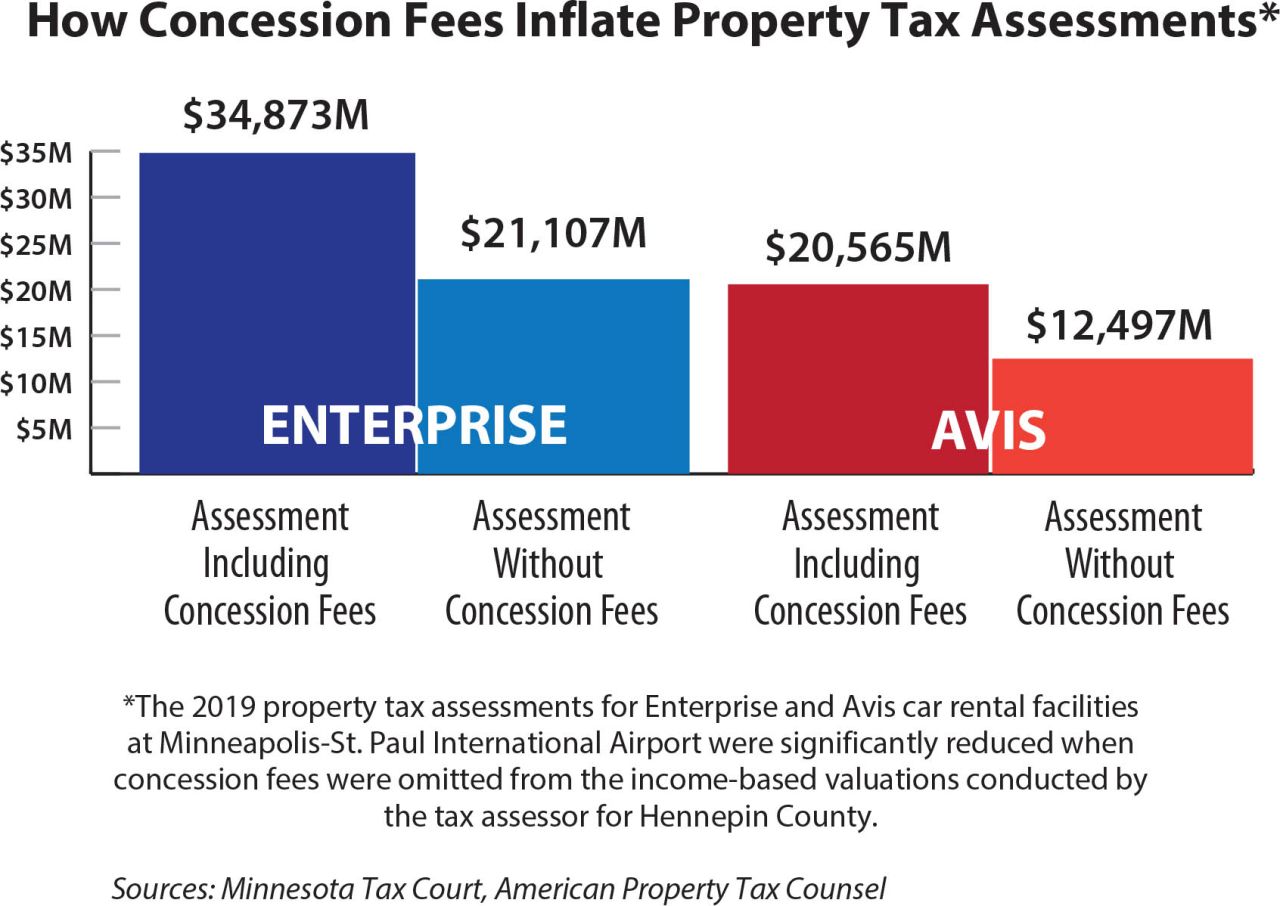
Jaye Calhoun and Divya Jeswant of Kean Miller LLP on an assessment strategy that may help you trim your property tax bill.
Few states impose property tax on intangible assets such as a trade name, franchise, goodwill and the like. Indeed, some office buildings, industrial properties and big-box stores don't derive significant value from intangibles in the first place.
Intangibles are a significant income generator for many hotels, casinos, restaurants and other properties, however. For these assets, assessors are required to identify and exclude the value attributable to those nontaxable intangibles. The proper method to do so has been the subject of much debate.
Fortunately for taxpayers, recent case law is helping to clarify best practices for isolating and removing value attributable to intangibles from commercial assessments. By following the examples of taxpayers who have successfully applied alternative approaches, property owners across the country may be able to exclude a larger portion of overall property value as intangible and, in turn, lower the property taxes on their business real estate.
Scaling Rushmore
Although some assessors persist in applying the cost approach, most valuation professionals consider the income approach most appropriate for valuing income-producing properties. That is because a property's past, present and future or projected income inevitably impact its valuation.
Many assessors have traditionally applied the "Rushmore Approach" to exclude the value of intangibles from an income-based valuation. This essentially deducts management and franchise fees from a property's net income, treating those amounts as a proxy for the value of intangibles.
Many taxpayers reject the notion that the Rushmore Approach can account for the full value of intangibles. Some of these property owners and their appraisers have countered with the "Business Enterprise Approach," which seeks to remove the often significantly higher revenue generated by intangible assets. This approach is sometimes called the "Income-Parsing Approach" because it requires going-concern income attributable to intangibles to be parsed and stripped from taxable property income.
A spate of decisions over the last few years, particularly concerning hotel valuation, has created a growing momentum favoring the Business Enterprise Approach. Taxpayers should be aware of the potential for significant tax savings with this approach.
Business enterprise successes
The most significant recent cases in which taxpayers successfully argued for using the Business Enterprise Approach are in two states known for high property taxes: Florida and California.
The first is Singh vs. Walt Disney Parks and Resorts U.S. Inc., a 2020 case dealing with the valuation of the Disney Yacht & Beach Club Resort adjacent to Epcot. A Florida appellate court categorically ruled that the Rushmore Approach fails to remove all intangible business value from an assessment. The court was simply unconvinced by the assessor's arguments that deductions for franchise and management fees can remove the entire intangible business value.
Another encouraging decision occurred in 2023, SHR St. Francis LLC vs. City and County of San Francisco. A California appeals court considered various income streams of the Westin St. Francis hotel, including its management agreement, income from cancellations, no-shows and attritions, in-room movies, and guest laundry services.
The court held that it was insufficient to simply deduct the management fees because income from a nontaxable, intangible asset like a management agreement should include both a "return of" and a "return on" that asset. In other words, the owner would expect to generate a profit, or income-based value over and above the cost of the management agreement. The court found that the assessor failed to present evidence that the management agreement's value did not exceed management fees.
In dealing with the remaining items, the court drew a dividing line between "intangible attributes of real property" that merely allow the taxable property to generate income (cancellations/no shows/attritions) and are therefore includible vs. "intangible assets and rights of the business operation" utilizing the real property. These latter assets and rights, including in-room movies and guest laundry services, relate to the intangible business operation and are, therefore ,excludible from income-based, taxable property value.
Another widely reported decision from 2023 is Olympic and Georgia Partners LLC vs. County of Los Angeles. The appellate court in this case pointed out a key flaw in the Rushmore Approach. That it is unlikely the deduction of franchise and management fees could fully account for the value of intangibles because no owner would normally agree to fees "so high as to account completely for all intangible benefits to a hotel owner."
Half Moon Bay legacy
Several recent decisions cite SHC Half Moon Bay LLC vs. County of San Mateo, a 2014 California case involving the Ritz Carlton Half Moon Bay Hotel's workforce, leasehold interest in the employee parking lot, and agreement with a golf course operator. The appellate court explicitly acknowledged that the deduction of management and franchise fees from the hotel's projected revenue stream did not properly identify and exclude intangible assets.
Taxpayers throughout the country have successfully made these same arguments. In 1300 Nicollet LLC vs. County of Hennepin, a Minnesota court in 2023 took stock of case law across the country and observed that although the two methods have been competing for 20 years, there is an emerging preference for the Business Enterprise Approach and increasing skepticism of the Rushmore Approach.
Some states such as New Jersey continue to rigidly administer the Rushmore Approach, while other states consistently uphold the Business Enterprise Approach, at least in recent years. Yet other states view both methods as potentially reasonable for an assessor to apply; some of those cases may have more to do with the standard of proof during appellate review. There are also states such as Louisiana in which the issue is yet to be dealt with judicially, arguably giving taxpayers an opportunity to get ahead of the curve.
Clearly, taxpayers and their commercial appraisers should determine whether the assessor has properly excluded maximal value for intangibles in valuing their income-producing properties for property tax purposes. In particular, appropriately applying the Business Enterprise Approach can generate significant property tax savings on commercial real estate and may be worth pursuing.
Deck - Summary for use on blog & category landing pages
-
Jaye Calhoun and Divya Jeswant of Kean Miller LLP on an assessment strategy that may help you trim your property tax bill.